Healthy eating for breastfeeding
Your body is well prepared for feeding your newborn baby. During the middle stages of your pregnancy it stored energy ready to begin producing breast milk as soon as your baby is born. In fact you may have already noticed, in the later part of your pregnancy, a thickish milk (colostrum) leaking from your breasts. Colostrum nourishes your baby for the first 3 to 5 days of its life until your breast milk is in full production. The antibodies in breast milk will provide your baby with protection against any infections over the duration of breast feeding.
Breast milk alone is the best food for your baby for the first 6 months. Your breast milk is specifically suited to your baby’s growth needs. At the beginning of a feed your milk is lower in fat, but after you ‘let-down’ the fat content increases. Suckle on demand to ensure you maintain enough breast milk to meet your baby’s growth needs.
Table: Special points about nutrition for breastfeeding women
| The changes |
Special points about nutrition |
| Your body needs even more energy than when you were pregnant to produce milk for your baby. You may feel tired, hungry and thirsty! |
- Eat to your appetite, choosing foods of high nutritional quality. (Refer to the food wheel below).
- Drink well over the day. Try to drink 8 to 10 glasses of water, milk or juice.
- Rest whenever possible.
|
| Your milk is providing all the minerals needed for the development of your baby's bones and teeth. |
- You require 1200 mg of calcium to meet this need and maintain your own bone health.
For example:
2.5 cups low fat milk 875 mg
1 cube cheese 260 mg
1 orange 90 mg
1/2 cup of broccoli 80 mg
Total 1265 mg
|
| Remember that your milk can carry drugs such as alcohol and caffeine across to your baby. It is more difficult for your baby to break these down and get rid of them |
- Always check with your doctor before taking medications.
- Limit your alcohol and caffeine intake.
|
| Weight loss appears to be individual. Some people are less efficient at using energy than others. Watch and adjust your meal intake accordingly. |
- If you are losing weight quickly, eat more foods of high nutritional quality.
- If you fail to lose or actually begin to gain weight, choose foods high in nutritional quality, and limit your fat and sugar intake.
|
| Maintain your fitness. |
- Exercise regularly – for example walking, cycling or swimming.
|
Food wheel
A pattern for daily food choices in pregnancy.
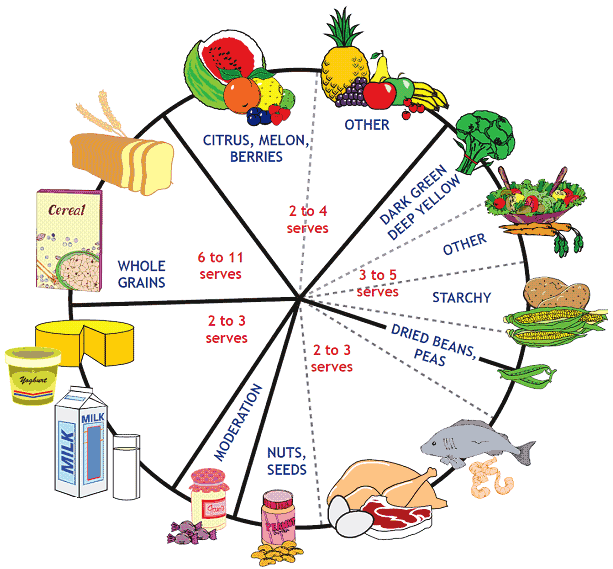
Breads and cereals
One serve is:
- 1 slice bread
- 2 large or 4 small crackers
- half a cup of cooked rice
- half a cup of cooked pasta
- two thirds of a cup of breakfast cereal
- half a muffin
- half a bagel.
Fruits
One serve is:
- average piece of whole fruit
- a melon wedge
- 180 ml fruit juice
- half a cup berries, sliced or cooked fruit
- one quarter of a cup of dried fruit
Vegetables
One serve is:
- half a cup of cooked or raw vegetables
- 1 cup of raw leafy vegetables.
Milk, cheese and yoghurt
One serve is:
- 1 cup of milk
- 3 cm cube of cheese
- 20 gram carton of yoghurt.
Meat, poultry, fish, eggs
Total of 150 to 200 grams daily
Alcohol
None
Fats, sweets
Keep to a minimum.
Where to get help
Breastfeeding Centre of WA
- Counselling and appointments 8.00am to 4.00pm Monday to Friday
- Phone: (08) 6458 1844
- More information about Breastfeeding Centre of WA
Australian Breastfeeding Association (ABA)
- National Breastfeeding Helpline available 24 hours, 7 days a week
- Phone: 1800 mum 2 mum (1800 686 268)
- Visit the ABA website (external site)
Ngala Parenting Line
- Phone: (08) 9368 9368 – 8.00am to 8.00pm 7 days a week
- Outside metro area – Free call 1800 111 546 (free from land line only)
- Visit the Ngala website (external site)
You can also:
Acknowledgements
Breastfeeding Centre of WA
This publication is provided for education and information purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical care. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not imply endorsement and is not intended to replace advice from your healthcare professional. Readers should note that over time currency and completeness of the information may change. All users should seek advice from a qualified healthcare professional for a diagnosis and answers to their medical questions.